Высококачественное лабораторное оборудование для сушки распылением 1,5 л
& nbsp; Лабораторные весы с распылительной сушилкой подходят для производства в университетах, исследовательских институтах и на предприятиях пищевой и фармацевтической химии. & nbsp;
A bioreactor is a device used in biological reaction processes, which plays a vital role in the fields of pharmaceuticals, food, environmental engineering, etc. The main function of a bioreactor is to provide a suitable environment for biological cells, microorganisms or biocatalysts such as enzymes to carry out biochemical reactions and thus produce target products. This article will introduce the definition, types, working principles, components, application fields, advantages and challenges of bioreactors in detail.
A bioreactor is a closed container used for biological processes, in which microorganisms, plant cells or animal cells are cultured to carry out a series of biochemical reactions. By controlling parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen and stirring speed, the bioreactor can provide the most suitable environmental conditions to promote the growth and metabolism of biocatalysts, thereby producing the desired biological products, such as drugs, enzymes, antibiotics, vaccines, food additives, etc.

The working principle of bioreactor is based on providing a suitable growth environment so that biocatalysts can carry out biochemical reactions under optimal conditions. Its core principles include:
The reactor body is the core part of the bioreactor, usually made of corrosion-resistant, stainless steel or glass materials, with good airtightness and pressure resistance. Its internal design needs to consider the characteristics of the reactants and the reaction conditions to provide the best biological reaction environment.
The stirring system is used to provide uniform mixing to ensure that the biocatalyst is fully in contact with the culture medium. The stirring system includes two forms: mechanical stirring and gas lifting. The appropriate stirring method is selected according to the specific application.
The control system is used to monitor and adjust various parameters of the bioreactor, such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, stirring speed, etc. Modern bioreactors are usually equipped with advanced automated control systems that can monitor and adjust reaction conditions in real time to ensure the stability and efficiency of the biological process.
The ventilation system is used to provide oxygen or other gases required for the reaction to maintain the dissolved oxygen content in the culture medium. The ventilation system includes components such as air pumps, gas distributors and gas filters, which can accurately control the flow and distribution of gases.
The sampling and discharge system is used to collect samples and discharge waste during the reaction process to ensure the smooth progress of the biological reaction. The sampling system needs to have good airtightness and sterility to avoid sample contamination and cross infection.
In the pharmaceutical industry, bioreactors are widely used in drug production, vaccine manufacturing, and antibody preparation. For example, they are used to produce antibiotics, monoclonal antibodies, insulin and other drugs to ensure the high efficiency and purity of the drugs.
In the food industry, bioreactors are used to produce products such as food additives, enzyme preparations and fermented foods. For example, they are used to produce food additives such as yeast, lactic acid bacteria, and monosodium glutamate to improve the flavor and nutritional value of food.
In the field of environmental engineering, bioreactors are used in processes such as sewage treatment and waste gas purification. For example, they are used to degrade organic matter in wastewater, remove heavy metals, and degrade pollutants in waste gas to reduce environmental pollution and protect the ecological environment.
In the field of bioenergy, bioreactors are used to produce products such as biofuels and biomass energy. For example, they are used to produce alternative energy sources such as biodiesel, ethanol, and methane to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and achieve sustainable energy development.
Bioreactors can provide the best growth environment, promote efficient metabolism and growth of biocatalysts, and thus achieve efficient production. By optimizing reaction conditions and control parameters, production efficiency and product quality can be significantly improved.
Modern bioreactors are equipped with advanced automated control systems that can monitor and adjust reaction conditions in real time to ensure the stability and efficiency of biological processes. By precisely controlling parameters such as temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen, precise regulation of biological processes can be achieved.
Bioreactors are suitable for a variety of biological processes, including microbial fermentation, cell culture, enzyme reactions, etc. Whether in the fields of pharmaceuticals, food, environmental engineering, or bioenergy, bioreactors can provide effective solutions to meet different application requirements.
The biological processes of bioreactors usually have lower energy consumption and environmental pollution, and are more environmentally friendly and sustainable than traditional chemical reactions. For example, by degrading organic matter through microorganisms, pollutants in wastewater can be effectively reduced and environmental pollution can be reduced.
The automated control system of the bioreactor needs to precisely control multiple parameters to ensure the stability and efficiency of the biological process. This places high demands on the design and operation of the control system, and requires professional technical knowledge and operating experience.
During the biological reaction process, biological contamination problems may occur, such as bacteria, viruses and other contaminants entering the reactor, affecting the normal progress of the biological process. Strict aseptic operation and monitoring measures need to be taken to ensure the aseptic environment of the bioreactor.
The design and manufacturing costs of bioreactors are high, especially large-scale industrial-grade bioreactors, which require a lot of money for equipment procurement, installation and maintenance. This places high demands on the capital investment and operation management of enterprises.
OLLITAL Technology is committed to providing high-quality bioreactor equipment, with many years of industry experience and a professional technical team. We focus on product research and development and innovation, continuously improve the performance and reliability of equipment, and meet the diverse needs of customers.
Our company not only provides bioreactor equipment, but also provides a full set of solutions such as material pretreatment and fermentation post-treatment. We are committed to providing customers with one-stop services for biological processes, from equipment selection, installation and commissioning to operation training and maintenance, to ensure that customers can produce efficiently and stably.
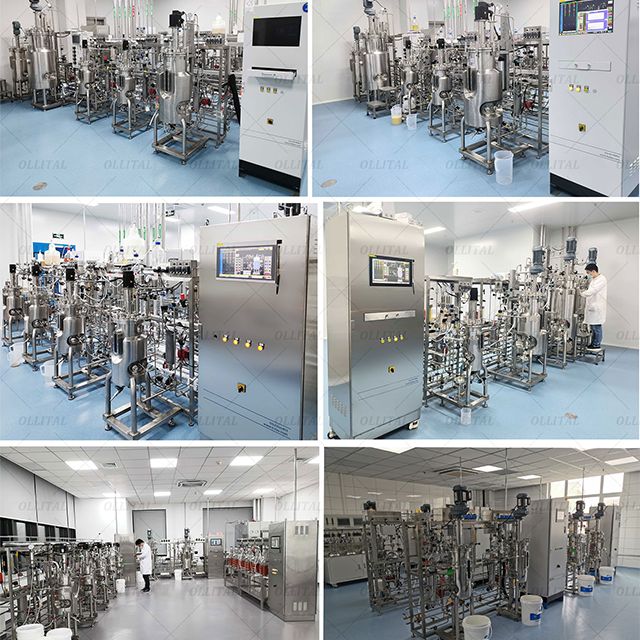

As an efficient and controllable bioprocess equipment, bioreactors are widely used in pharmaceutical, food, environmental engineering and other fields. By understanding the definition, types, working principles, application fields and advantages of bioreactors, we can better utilize this advanced technology to improve production efficiency and product quality. If you have any questions about bioreactors or need further technical support, please feel free to contact us and we will serve you wholeheartedly.
 Интернет Сервис
Интернет Сервис +86 15960821529
+86 15960821529 kevin@ollital.com
kevin@ollital.com kevinollital@gmail.com
kevinollital@gmail.com +86 15960821529
+86 15960821529 +8615960821529
+8615960821529